Category: Other
EPA Announces New 5-Year Plan to Accelerate Restoration of the Great Lakes
EPA Announces New 5-Year Plan to Accelerate Restoration of the Great Lakes
josterme01
Fri, 11/29/2024 – 9:22 am

Today, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency announced an updated action plan for federal agencies and their partners under the Great Lakes Restoration Initiative to restore and protect the Great Lakes over the next five years. The plan was informed by extensive public engagement and consultation with Great Lakes Tribes and states.
Last summer, EPA and its federal partners received more than 3,500 suggestions from the public on priorities for Action Plan IV through five public engagement sessions across the Great Lakes basin and two virtual engagement sessions. In addition, EPA released a draft of the GLRI Action Plan IV for public input earlier this year. Over 40 sets of public input from organizations and individuals were received and incorporated into GLRI Action Plan IV.
Action Plan IV outlines the GLRI’s priorities and goals for 2025 to 2029 in five focus areas:
- Toxic Substances and Areas of Concern;
- Invasive Species;
- Nonpoint Source Pollution;
- Habitat and Species; and
- Foundations for Future Restoration Actions.
The GLRI has been a catalyst for unprecedented federal agency coordination that has accordingly produced unprecedented results. Six U.S. Areas of Concern have been delisted since GLRI’s start and the 24 remaining Areas of Concern have moved dramatically closer to their delisting. This activity reflects a major change from the 25 years before the GLRI, when only one Area of Concern was cleaned up and delisted. GLRI resources have also been used for projects that have prevented over 2.3 million pounds of phosphorus from entering the Great Lakes between 2015 and 2022 and have reduced the phosphorus runoff contribution to harmful algal blooms in western Lake Erie, Saginaw Bay and Green Bay.
The GLRI also produces economic benefits — a 2018 University of Michigan study showed that every dollar of federal spending on GLRI projects between 2010 and 2016 will produce $3.35 in additional economic activity in the Great Lakes region through 2036.
In the coming weeks, a web-version of Action Plan IV will be available.
EPA Announces New 5-Year Plan to Accelerate Restoration of the Great Lakes
EPA Announces New 5-Year Plan to Accelerate Restoration of the Great Lakes
josterme01
Fri, 11/29/2024 – 9:22 am
Aerial view of a GLRI project which installed submerged rubble ridges at Illinois Beach State Park. Photo credit: US Army Corps of Engineers
Today, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency announced an updated action plan for federal agencies and their partners under the Great Lakes Restoration Initiative to restore and protect the Great Lakes over the next five years. The plan was informed by extensive public engagement and consultation with Great Lakes Tribes and states.
Last summer, EPA and its federal partners received more than 3,500 suggestions from the public on priorities for Action Plan IV through five public engagement sessions across the Great Lakes basin and two virtual engagement sessions. In addition, EPA released a draft of the GLRI Action Plan IV for public input earlier this year. Over 40 sets of public input from organizations and individuals were received and incorporated into GLRI Action Plan IV.
GLRI Action Plan IV
Action Plan IV outlines the GLRI’s priorities and goals for 2025 to 2029 in five focus areas:
- Toxic Substances and Areas of Concern;
- Invasive Species;
- Nonpoint Source Pollution;
- Habitat and Species; and
- Foundations for Future Restoration Actions.
The GLRI has been a catalyst for unprecedented federal agency coordination that has accordingly produced unprecedented results. Six U.S. Areas of Concern have been delisted since GLRI’s start and the 24 remaining Areas of Concern have moved dramatically closer to their delisting. This activity reflects a major change from the 25 years before the GLRI, when only one Area of Concern was cleaned up and delisted. GLRI resources have also been used for projects that have prevented over 2.3 million pounds of phosphorus from entering the Great Lakes between 2015 and 2022 and have reduced the phosphorus runoff contribution to harmful algal blooms in western Lake Erie, Saginaw Bay and Green Bay.
The GLRI also produces economic benefits — a 2018 University of Michigan study showed that every dollar of federal spending on GLRI projects between 2010 and 2016 will produce $3.35 in additional economic activity in the Great Lakes region through 2036.
In the coming weeks, a web-version of Action Plan IV will be available.
Fri, 11/29/2024 – 9:22 am
Keywords
Aerial view of a GLRI project which installed submerged rubble ridges at Illinois Beach State Park. Photo credit: US Army Corps of Engineers
Today, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency announced an updated action plan for federal agencies and their partners under the Great Lakes Restoration Initiative to restore and protect the Great Lakes over the next five years. The plan was informed by extensive public engagement and consultation with Great Lakes Tribes and states.
Last summer, EPA and its federal partners received more than 3,500 suggestions from the public on priorities for Action Plan IV through five public engagement sessions across the Great Lakes basin and two virtual engagement sessions. In addition, EPA released a draft of the GLRI Action Plan IV for public input earlier this year. Over 40 sets of public input from organizations and individuals were received and incorporated into GLRI Action Plan IV.
GLRI Action Plan IV
Action Plan IV outlines the GLRI’s priorities and goals for 2025 to 2029 in five focus areas:
- Toxic Substances and Areas of Concern;
- Invasive Species;
- Nonpoint Source Pollution;
- Habitat and Species; and
- Foundations for Future Restoration Actions.
The GLRI has been a catalyst for unprecedented federal agency coordination that has accordingly produced unprecedented results. Six U.S. Areas of Concern have been delisted since GLRI’s start and the 24 remaining Areas of Concern have moved dramatically closer to their delisting. This activity reflects a major change from the 25 years before the GLRI, when only one Area of Concern was cleaned up and delisted. GLRI resources have also been used for projects that have prevented over 2.3 million pounds of phosphorus from entering the Great Lakes between 2015 and 2022 and have reduced the phosphorus runoff contribution to harmful algal blooms in western Lake Erie, Saginaw Bay and Green Bay.
The GLRI also produces economic benefits — a 2018 University of Michigan study showed that every dollar of federal spending on GLRI projects between 2010 and 2016 will produce $3.35 in additional economic activity in the Great Lakes region through 2036.
In the coming weeks, a web-version of Action Plan IV will be available.
Fri, 11/29/2024 – 9:22 am
Keywords
Drop-in at the Bridge gets huge financial boost
(By Liz Small) Drop-in at The Bridge has received a huge financial boost, thanks to an Ontario Trillium Seed Grant, in the amount of $88,000. To read the entire article … Continue reading Drop-in at the Bridge gets huge financial boost
The post Drop-in at the Bridge gets huge financial boost appeared first on Kincardine Independent.
Soil Health Improvements in Western New York Farm Increase Economic Gain for Farmers
Soil Health Improvements in Western New York Farm Increase Economic Gain for Farmers
josterme01
Tue, 11/26/2024 – 9:45 am
The Great Lakes are vital, providing drinking water for millions of people, but cropland in the basin contributes to excess nutrients and phosphorus entering the lakes. Farmers care about protecting water quality, but they face challenges in adopting conservation practices due to tight profit margins, concerns about yield impacts, insecure leases, and complexities with integrating conservation into their current management systems. While these practices are crucial for improving soil health and reducing nutrient runoff, farmers also need to see them as practical and profitable to decide to implement them. Through this project, American Farmland Trust (AFT) aimed to encourage farmers in the Genesee River Watershed to adopt soil regenerative management systems. We accomplished this by expanding a farmer-to-farmer demonstration network, gathering and sharing data on the benefits of regenerative agriculture, and fostering better relationships between landowners and farmers.
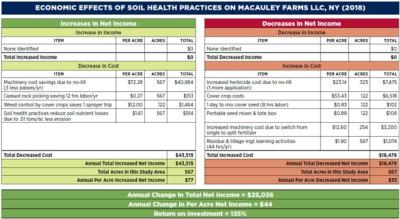
One highlight from this project was working with John Macauley of Macauley Farm – a multi-generation beef and crop farm stewarding 1,106 acres in the Genesee River watershed. Through their conservation practices of no-till, planting cover crops, and split fertilizer application, the Macauleys are saving around $72 per acre annually in machinery and labor expenses, while reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 69 percent. John is also happy to not be picking rocks anymore, which were kicked up by tillage.
“I am focused on building my soil health and letting nature do some of the work for me,” John says. “I may not be setting records for high yields, but at the end of the day, I’ve got more money in my pocket instead of shelling it all out upfront.”
John believes that continuing to find ways to improve his soil health will provide even greater returns in the future as he experiments with cover crop mixes to supply nutrients, thereby reducing reliance on inorganic N, P, and micronutrients. American Farmland Trust is grateful to have Macauley Farm as a member of the Genesee River Demonstration Farms Network, where John shares his knowledge and experience with his peers to help spread the adoption of soil health practices throughout the watershed.
To see more examples of economic case studies focused on soil health, and for more information on the Genesee River Demonstration Farm Network please visit our project webpage.
Soil Health Improvements in Western New York Farm Increase Economic Gain for Farmers
Soil Health Improvements in Western New York Farm Increase Economic Gain for Farmers
josterme01
Tue, 11/26/2024 – 9:45 am
Working with John Macauley and a Cornell Cooperative Extension Ag Economist, AFT created a partial budget to analyze the marginal benefits and costs of adopting no-till, cover crops, and nutrient management on the Macauley Farm. As a result of the three soil health practices, John’s net income increased by $44 per acre per year or by $25,036 annually on the 567-acre study area, achieving a 135% return on investment.
The Great Lakes are vital, providing drinking water for millions of people, but cropland in the basin contributes to excess nutrients and phosphorus entering the lakes. Farmers care about protecting water quality, but they face challenges in adopting conservation practices due to tight profit margins, concerns about yield impacts, insecure leases, and complexities with integrating conservation into their current management systems. While these practices are crucial for improving soil health and reducing nutrient runoff, farmers also need to see them as practical and profitable to decide to implement them. Through this project, American Farmland Trust (AFT) aimed to encourage farmers in the Genesee River Watershed to adopt soil regenerative management systems. We accomplished this by expanding a farmer-to-farmer demonstration network, gathering and sharing data on the benefits of regenerative agriculture, and fostering better relationships between landowners and farmers.
One highlight from this project was working with John Macauley of Macauley Farm – a multi-generation beef and crop farm stewarding 1,106 acres in the Genesee River watershed. Through their conservation practices of no-till, planting cover crops, and split fertilizer application, the Macauleys are saving around $72 per acre annually in machinery and labor expenses, while reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 69 percent. John is also happy to not be picking rocks anymore, which were kicked up by tillage.
“I am focused on building my soil health and letting nature do some of the work for me,” John says. “I may not be setting records for high yields, but at the end of the day, I’ve got more money in my pocket instead of shelling it all out upfront.”
John believes that continuing to find ways to improve his soil health will provide even greater returns in the future as he experiments with cover crop mixes to supply nutrients, thereby reducing reliance on inorganic N, P, and micronutrients. American Farmland Trust is grateful to have Macauley Farm as a member of the Genesee River Demonstration Farms Network, where John shares his knowledge and experience with his peers to help spread the adoption of soil health practices throughout the watershed.
To see more examples of economic case studies focused on soil health, and for more information on the Genesee River Demonstration Farm Network please visit our project webpage.
Tue, 11/26/2024 – 9:45 am
Keywords
Working with John Macauley and a Cornell Cooperative Extension Ag Economist, AFT created a partial budget to analyze the marginal benefits and costs of adopting no-till, cover crops, and nutrient management on the Macauley Farm. As a result of the three soil health practices, John’s net income increased by $44 per acre per year or by $25,036 annually on the 567-acre study area, achieving a 135% return on investment.
The Great Lakes are vital, providing drinking water for millions of people, but cropland in the basin contributes to excess nutrients and phosphorus entering the lakes. Farmers care about protecting water quality, but they face challenges in adopting conservation practices due to tight profit margins, concerns about yield impacts, insecure leases, and complexities with integrating conservation into their current management systems. While these practices are crucial for improving soil health and reducing nutrient runoff, farmers also need to see them as practical and profitable to decide to implement them. Through this project, American Farmland Trust (AFT) aimed to encourage farmers in the Genesee River Watershed to adopt soil regenerative management systems. We accomplished this by expanding a farmer-to-farmer demonstration network, gathering and sharing data on the benefits of regenerative agriculture, and fostering better relationships between landowners and farmers.
One highlight from this project was working with John Macauley of Macauley Farm – a multi-generation beef and crop farm stewarding 1,106 acres in the Genesee River watershed. Through their conservation practices of no-till, planting cover crops, and split fertilizer application, the Macauleys are saving around $72 per acre annually in machinery and labor expenses, while reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 69 percent. John is also happy to not be picking rocks anymore, which were kicked up by tillage.
“I am focused on building my soil health and letting nature do some of the work for me,” John says. “I may not be setting records for high yields, but at the end of the day, I’ve got more money in my pocket instead of shelling it all out upfront.”
John believes that continuing to find ways to improve his soil health will provide even greater returns in the future as he experiments with cover crop mixes to supply nutrients, thereby reducing reliance on inorganic N, P, and micronutrients. American Farmland Trust is grateful to have Macauley Farm as a member of the Genesee River Demonstration Farms Network, where John shares his knowledge and experience with his peers to help spread the adoption of soil health practices throughout the watershed.
To see more examples of economic case studies focused on soil health, and for more information on the Genesee River Demonstration Farm Network please visit our project webpage.
Tue, 11/26/2024 – 9:45 am
Keywords










